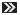| |||||||
| Search Forums |
| Advanced Search |
| Go to Page... |
 |
| Search this Thread |  841,915 views |
| | #1966 | |
| Senior - BHPian | Re: Scale Models - Aircraft, Battle Tanks & Ships Quote:
A couple of photos in your post can be easily mistaken for the real thing! Congratulations on another brilliant addition to your ever growing Indian fighter fleet. 1:43 Willys Jeep MB United Nations 86-201 Disclaimer - This probably just qualifies for this thread as the Willys Jeep was primarily built as a military vehicle, which was later the base for civilian Jeeps. The Willys MB, informally the Willys Jeep was an American designed, off-road four-wheel drive military light utility vehicles built in large numbers to a single standardized design for the United States and the Allies of World War II from 1941 until 1945. It was the world's first mass-produced light four-wheel drive motor vehicle and became the primary light-wheeled multi-role vehicle of the United States military and its allies.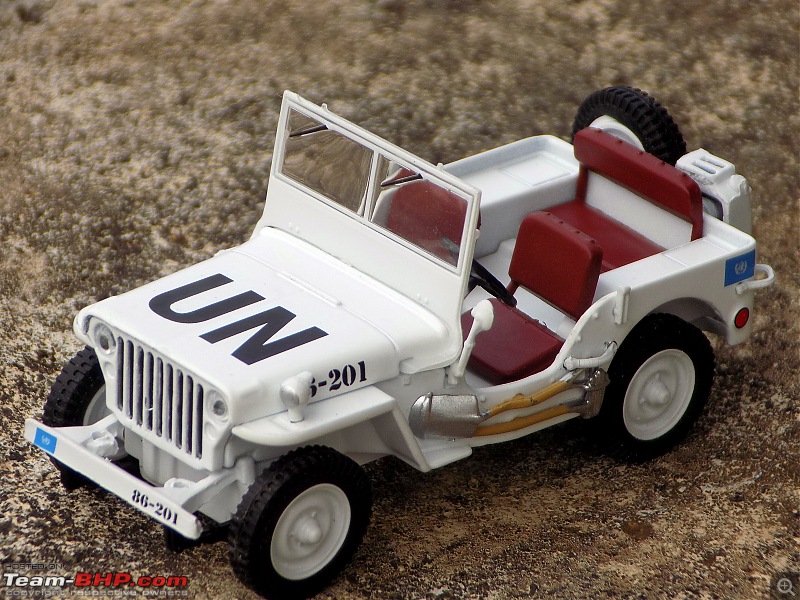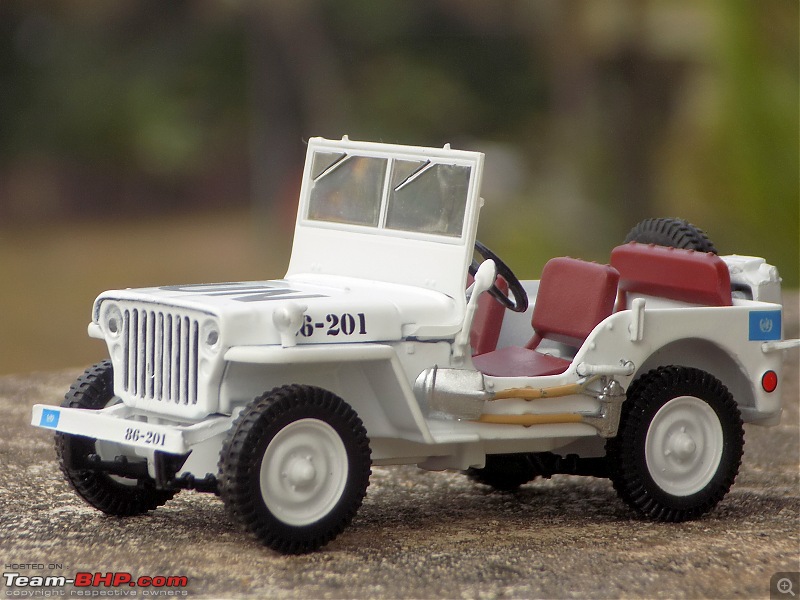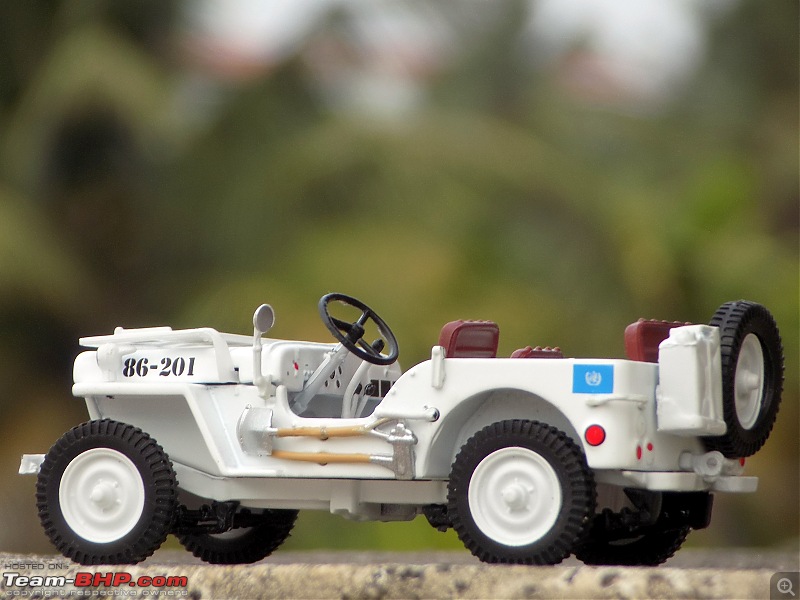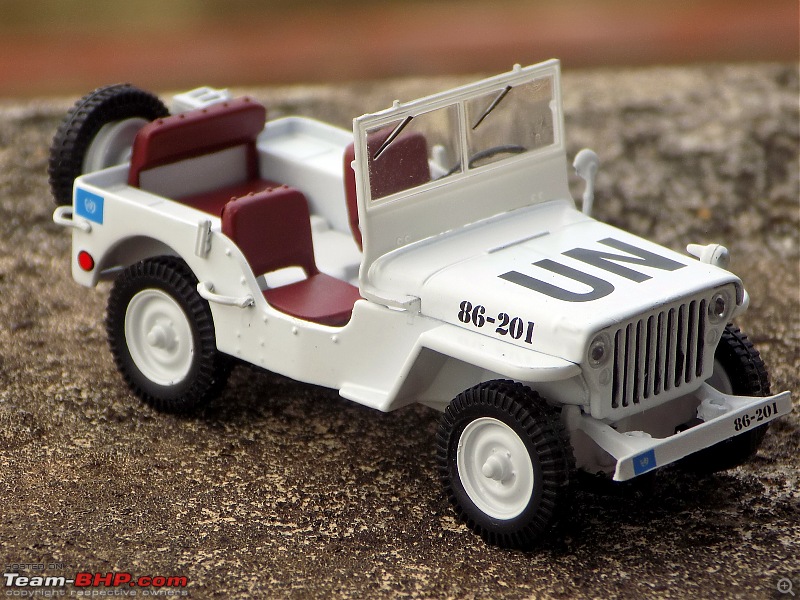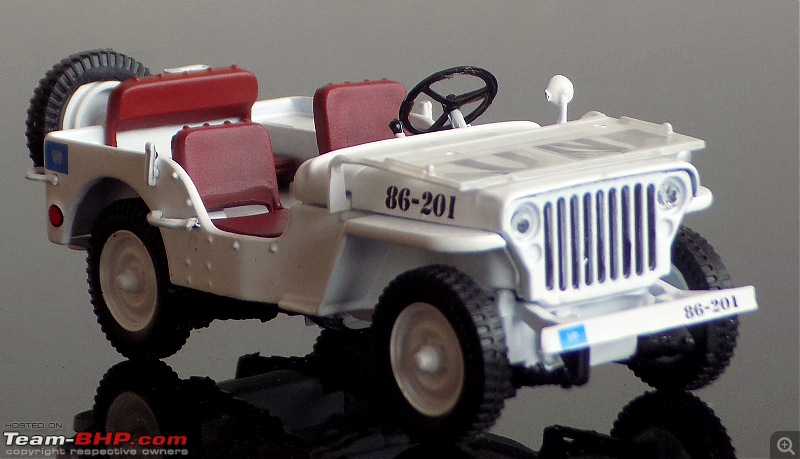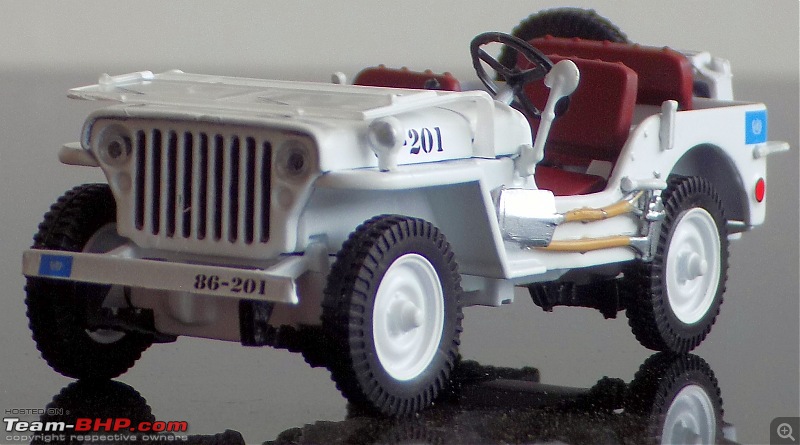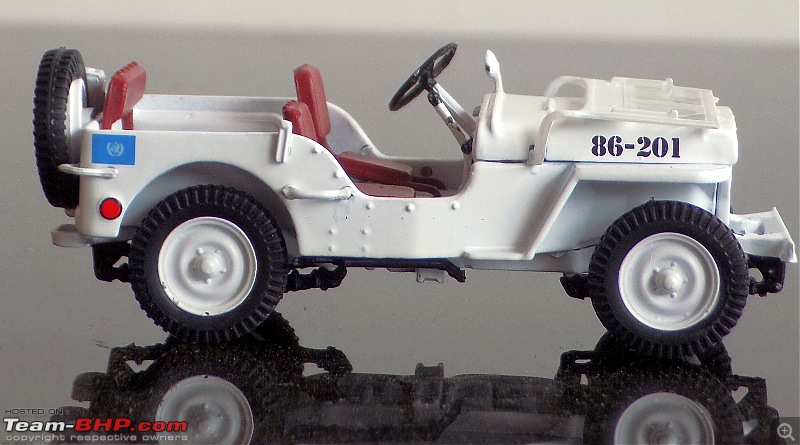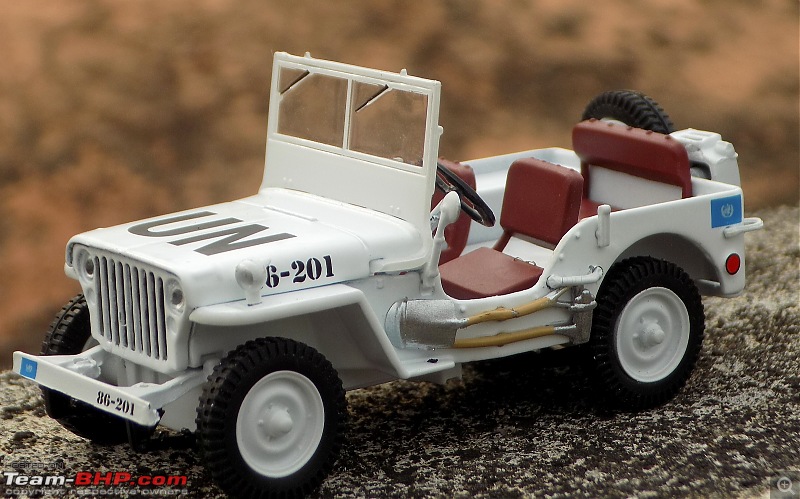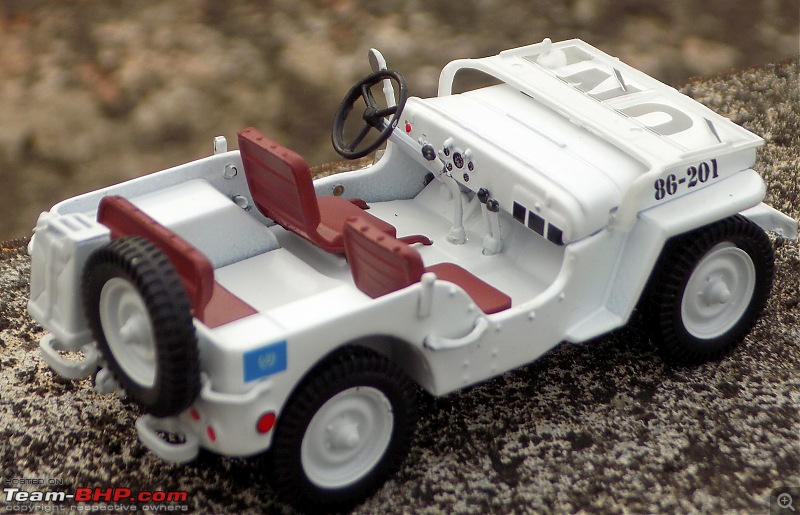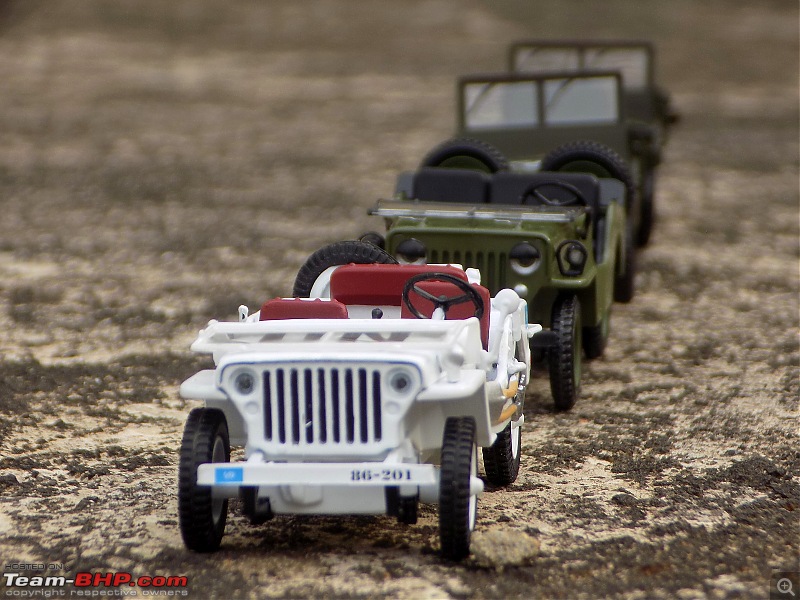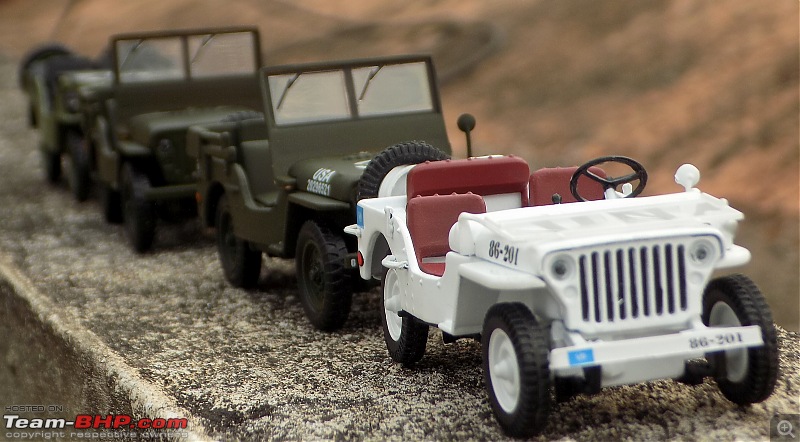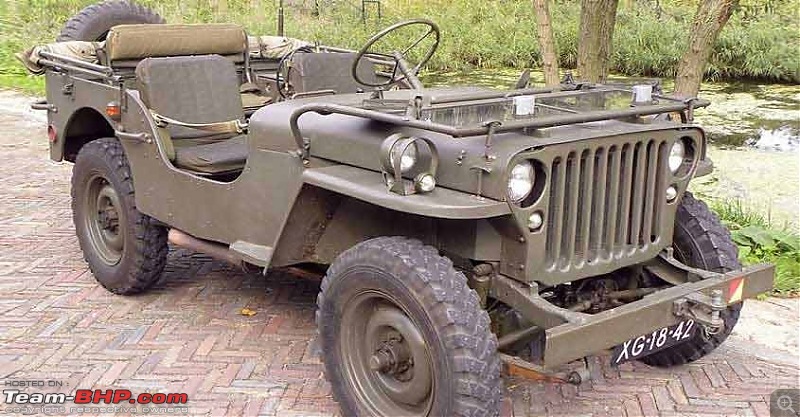                       Last edited by skanchan95 : 24th January 2023 at 16:40. | |
| |  (6)
Thanks (6)
Thanks
|
| The following 6 BHPians Thank skanchan95 for this useful post: | badboyscad, Foxbat, libranof1987, quantobigboot, sajands, V.Narayan |
| |
| | #1967 | ||
| Distinguished - BHPian  Join Date: Aug 2014 Location: Delhi-NCR
Posts: 4,330
Thanked: 72,462 Times
| Re: Scale Models - Aircraft, Battle Tanks & Ships Quote:
Quote:
| ||
| |  (1)
Thanks (1)
Thanks
|
| The following BHPian Thanks V.Narayan for this useful post: | badboyscad |
| | #1968 | |
| Distinguished - BHPian  Join Date: Aug 2014 Location: Delhi-NCR
Posts: 4,330
Thanked: 72,462 Times
| Re: Scale Models - Aircraft, Battle Tanks & Ships Dassault Mystere IV:: IAF, day fighter:: 1:72 scale, Fromm {a French-Belgian scale model brand} About 7 inches in length with a span of 6 inches. Top class details, finish and paint work. Assembled & painted by member @ Basuroy A worthy follow-on from the Dassault stables to the Ouragan or Toofani. Dassault was working hard in the 1950s to catch up, in fighter design, with the British, American and Russians not to mention the Swedes. Dassault wisely went step by step graduating to the Mystere II which was a swept wing version of the Ouragan taking top speed from 500 to 575 knots. Then they moved boldly to the Dassault IV an all new design fitting a 41 degree sharply swept wing with a thin profile at 7.5% thickness to chord ratio versus 9% for the Mystere II. This was matched with the Verdon 350 turbojet producing 3500 kgf. The Verdon itself was a derivative of the British Rolls Royce Tay. It followed the then common, simple to build, straight through air intake design. India wanted to equip its squadrons with a real transonic 600 knot fighter. The British were not willing to sell the Hawker Hunter even though we were their largest military aircraft customer. This political arrogance waffling between of supplying-not supplying remained a trait of that country versus us for the next 40 years. So, we went to the French. As soon as our contract was inked the British had a change of heart! The IAF purchased 67 Mystere IV. It also served with Israel & of course with France. Mystere vs Hunter – Hunter was the superior aircraft which is not to say the Mystere IV was poor. In the 1965 Indo-Pak conflict Mystere IV’s of the IAF shot down one L-19 artillery spotter aircraft and one F-104 Starfighter in a remarkable twist of events which killed the Mystere pilot, Sqn Leader Devvaya too. Our Mystere’s destroyed 2 C-130 transports, 3 F-104 Starfighter and 4 F-86 Sabres on the ground. Depicted here is a Mystere of Nos 1 Squadron, ‘The Tigers’ with nose art to match. Entered service in 1957. The Mystere's were withdrawn from service between 1973 & 1975. This outstanding model has been put together and carefully painted by Basu Roy. Photos by Bau Roy. Kudos to him. Quote:
Last edited by vb-saan : 26th January 2023 at 19:03. Reason: As requested | |
| |  (8)
Thanks (8)
Thanks
|
| The following 8 BHPians Thank V.Narayan for this useful post: | badboyscad, Foxbat, FrozeninTime, Jeroen, libranof1987, sajands, skanchan95, vb-saan |
| | #1969 | |||
| BHPian Join Date: May 2009 Location: NYC / Lucknow
Posts: 709
Thanked: 4,167 Times
| Re: Scale Models - Aircraft, Battle Tanks & Ships Quote:
Quote:
 Quote:
Some work in progress of my Su-27 cockpit, somehow enthusiasm is lacking these days to complete it. I'm not able to use spray paint because I live in a tiny apartment and brush painting such a huge model is a task with inconsistent results. 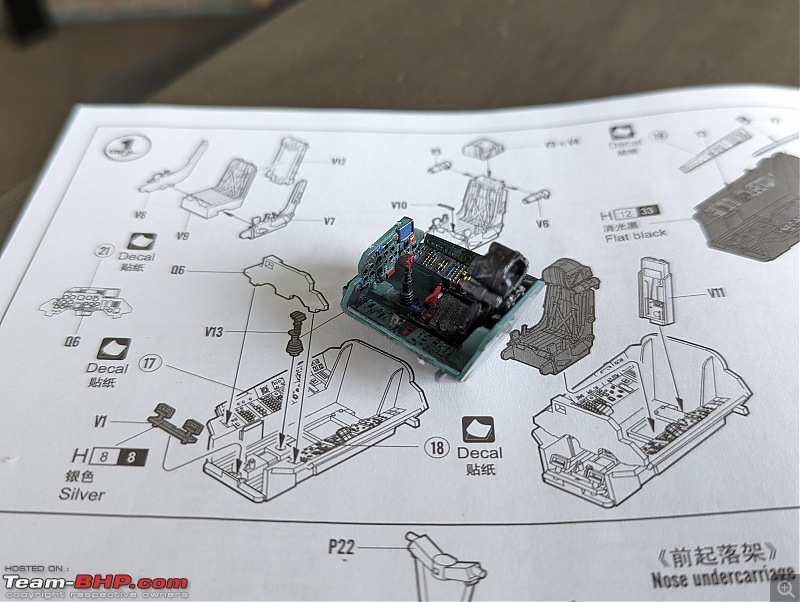  | |||
| |  (4)
Thanks (4)
Thanks
|
| The following 4 BHPians Thank Foxbat for this useful post: | badboyscad, Jeroen, skanchan95, V.Narayan |
| | #1970 | |
| Distinguished - BHPian  | Re: Scale Models - Aircraft, Battle Tanks & Ships Quote:
Very elegant looking plane. Not sure how many were produced. It seems that almost any aviation museum around the world has at least one Hunter. But these Mystere’s are pretty rare. There are still some Hunters being flown by enthusiast. And of course the awful 2015 Shoreham crash of a Hunter is still fresh in the minds of aviation enthusiast. Are there any airworthy Mystere’s about by any chance? Jeroen | |
| |  ()
Thanks ()
Thanks
|
| | #1971 | ||
| Distinguished - BHPian  Join Date: Aug 2014 Location: Delhi-NCR
Posts: 4,330
Thanked: 72,462 Times
| Re: Scale Models - Aircraft, Battle Tanks & Ships Quote:
 Your dedication is admirable. Honestly I could not manage it. Eagerly looking forward to the end product. Your dedication is admirable. Honestly I could not manage it. Eagerly looking forward to the end product.Quote:
The Harrier and Mystere boxes have been delivered. So soon I will insist on publishing another round of photos taken by me. The ones in the two posts above are courtesy Basu Roy. You can't stop a three year old from displaying his toys.  | ||
| |  (2)
Thanks (2)
Thanks
|
| The following 2 BHPians Thank V.Narayan for this useful post: | Foxbat, Jeroen |
| | #1972 | |
| BHPian Join Date: May 2009 Location: NYC / Lucknow
Posts: 709
Thanked: 4,167 Times
| Re: Scale Models - Aircraft, Battle Tanks & Ships Quote:
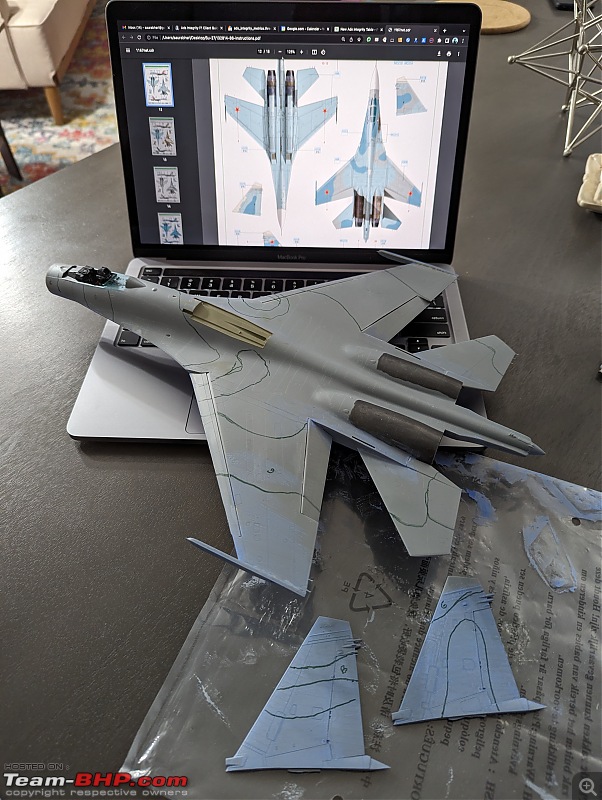 | |
| |  (3)
Thanks (3)
Thanks
|
| The following 3 BHPians Thank Foxbat for this useful post: | badboyscad, skanchan95, V.Narayan |
| | #1973 |
| Senior - BHPian | Re: Scale Models - Aircraft, Battle Tanks & Ships 1:250 Embraer KC-390 Millenium (Lupa) In 2007, the Embraer company of Brazil announced plans for a military cargolifter, originally the "KC-390", later the "C-390", to be derived from the Embraer 190 jetliner. As initially envisioned, the C-390 would use the wings, tail, engines and avionics of the E190 along with a new fuselage, providing a maximum payload of 19 tonnes (21 tons) -- placing the C-390 in the payload range of the C-130 Hercules. The primary target customer was the Brazilian Air Force (FAB). The design evolved into an effectively all-new aircraft with a maximum payload of 23 tonnes (25.3 tons), comfortably exceeding the 21.8 tonnes (24 tons) of the state-of-the-art C-130J. As introduced, the C-390 had a typical jet cargolifter configuration, with high swept wings, a high-bypass turbofan engine under each wing, a boxy fuselage with landing gear in sponsons, and a high tee tail with a tail loading ramp. The aircraft is powered by International Aero Engines (IAE) V2500-E5 turbofans, with thrust in the range of 100 kN (10,200 kgp / 22,500 lbf). The V2500 engines also powers the Airbus A320 CEO midsize jetliner family. The V2500-E5 engine was ruggedized, with a modified control system and an improved thrust reverser for short-field landing capability of the C-390. The cockpit features a Rockwell-Collins Pro Line Fusion system, with five large-screen displays and twin HUDs. The cockpit is compatible with night vision goggles, and the aircraft was fitted with a defensive countermeasures suite. The C-390 incorporates a fly-by-wire flight control system implemented by BAE Systems of the UK. The C-390's cargo compartment is 17.75 meters (58 feet 2 inches) long, 3.45 meters (11 feet 4 inches) wide, 2.9 meters (9 feet 6 inches) high forward of the wing, and 3.2 meters (10 feet 6 inches) high aft of the wing. Maximum payload of the C-390 is 26 tonnes (28.6 tons). One unusual feature is a movable pressure bulkhead that retracted garage door-style into the roof, and descended to seal the cargo cabin. When lowered, this sloping bulkhead reduced compartment length to 12.78 meters (41 feet 11 inches) at the ceiling. The KC-90 can carry up to 88 equipped troops or 66 paratroopers. Alternatively, it can carry up to seven standard cargo pallets, three tactical vehicles, a single LAV-25 combat vehicle, or a Sikorsky UH-60 Black Hawk helicopter. Baseline configuration featured an inflight refueling probe above the cockpit -- and for the tanker mission, a hose-drogue refueling pod under each wingtip. The refueling pods were supplied by Cobham Mission Equipment of the UK, being slightly altered from a standard Cobham product. The first of two C-390 prototypes was rolled out in October 2014, with initial flight on 3 February 2015. The second prototype performed its first flight on 28 April 2016, with the first production machine performing its initial flight on 9 October 2018. The first delivery to the Brazilian Air Force was in 2019, with 30 to be obtained by 2026 -- including the two prototypes, to be brought up to operational specs. In that same year, the designation was changed from KC-390 to C-390, the aircraft being given the name of "Millennium"; users flying it as a tanker will retain the KC-390 designation. Portugal, which is a partner in the C-390 program, committed to buying five in 2017, with an option for one more. A C-390 of the Brazilian Air Force is on static display at Aero India '23 and is apparently in the running for IAF's requirement of a new medium transport aircraft (along with the Airbus A400, LM C-130J & Kawasaki C-2). General characteristics Crew: Three flight crew (Two pilots, one loadmaster) Capacity: 80 troops / 74 stretchers and 8 attendants / 66 paratroopers / 7 463L master pallets / 6 463L master pallets and 36 troops Length: 35.2 m (115 ft 6 in) Wingspan: 35.05 m (115 ft 0 in) Height: 11.84 m (38 ft 10 in) Max takeoff weight: 86,999 kg (191,800 lb) Fuel capacity: 23,000 kg (50,700 lb), 35,000 kg (77,160 lb) with 3 aux. fuel tanks Useful lift: 26,000 kg (57,320 lb) Hold length × height × width: 18.5×3.0×3.4 m (60.6×9.8×11.3 ft) Powerplant: 2 × IAE V2500-E5 turbofans, 139.4 kN (31,330 lbf) thrust each Performance Maximum speed: 988 km/h (614 mph, 533 kn) Cruise speed: 870 km/h (540 mph, 470 kn) Mach 0.8 Stall speed: 193 km/h (120 mph, 104 kn) IAS Range: 5,820 km (3,610 mi, 3,140 nmi) with 14,000 kg (30,865 lb) payload Range alt: 2,820 km (1,520 nmi) with 23,000 kg (51,000 lb) payload Range alt2: 2,110 km (1,140 nmi) with 26,000 kg (57,320 lb) payload Ferry range: 8,500 km (5,300 mi, 4,600 nmi) max. with aux. fuel tanks; normal ferry 3,310 nmi, 6,130 km Service ceiling: 11,000 m (36,000 ft) Armament Hardpoints: 3 with a capacity of POD Optical / IR Rafael Litening II / IFR Cobham 900E Avionics Rockwell Collins Pro Line Fusion Systems and equipment RWR / chaff & flare (self-defense systems) DIRCM - Directional Infrared Countermeasures (self-defense systems) In-flight refueling system Dual HUD system Cabin lighting compatible with night vision systems CCDP - Continuously Computed Drop Point, an automated, accurate drop point calculation system[115] CDS - Container Delivery System[116] LVAD - Low Velocity Airdrop Delivery[116] EEPGS – Emergency Electric Power Generator System (type RAT or Ram Air Turbine)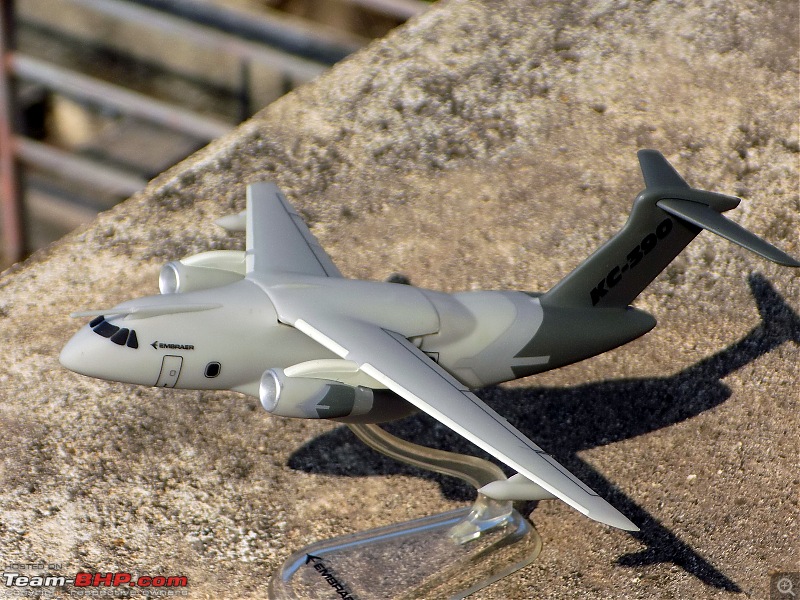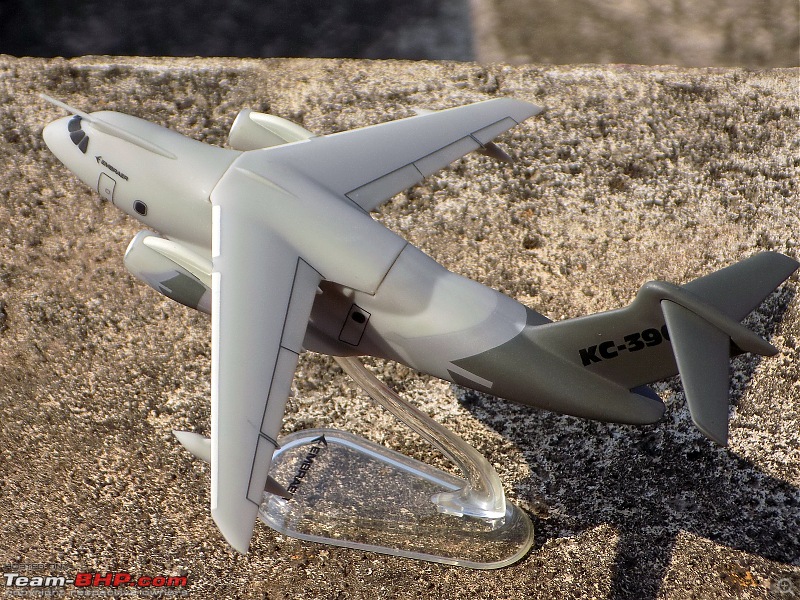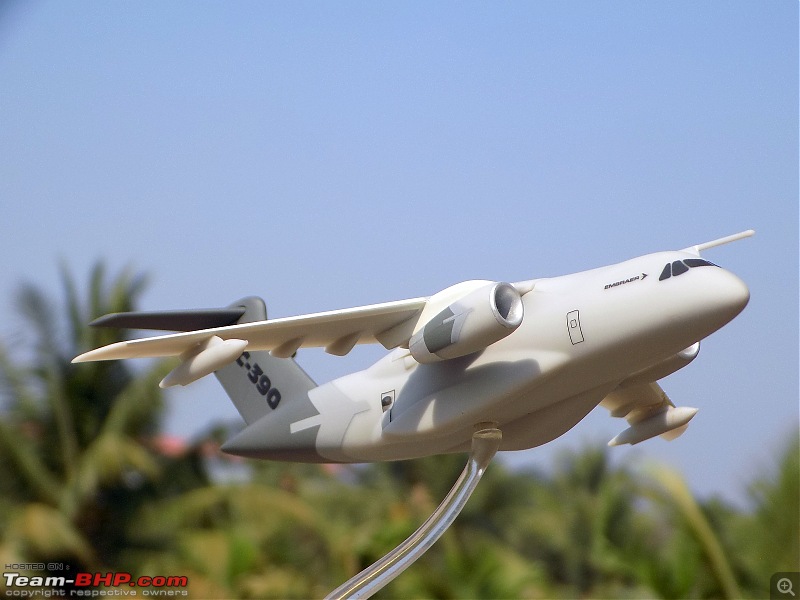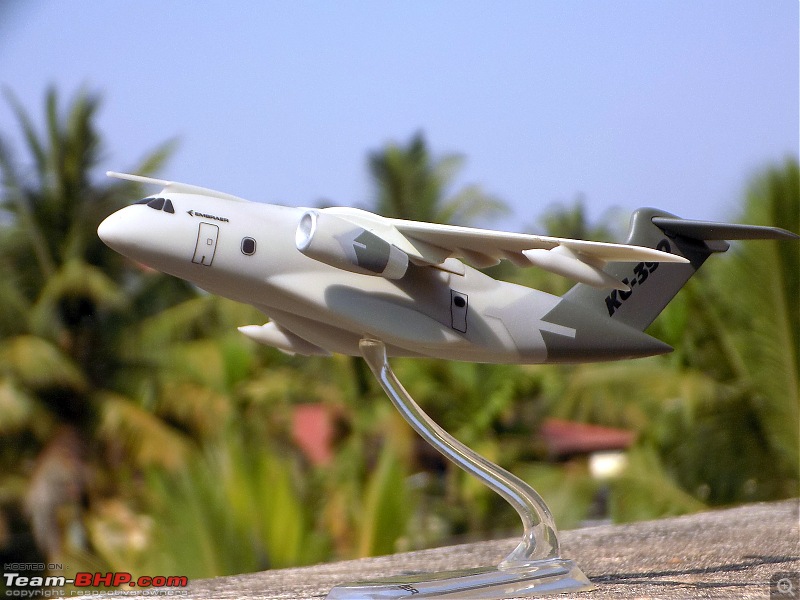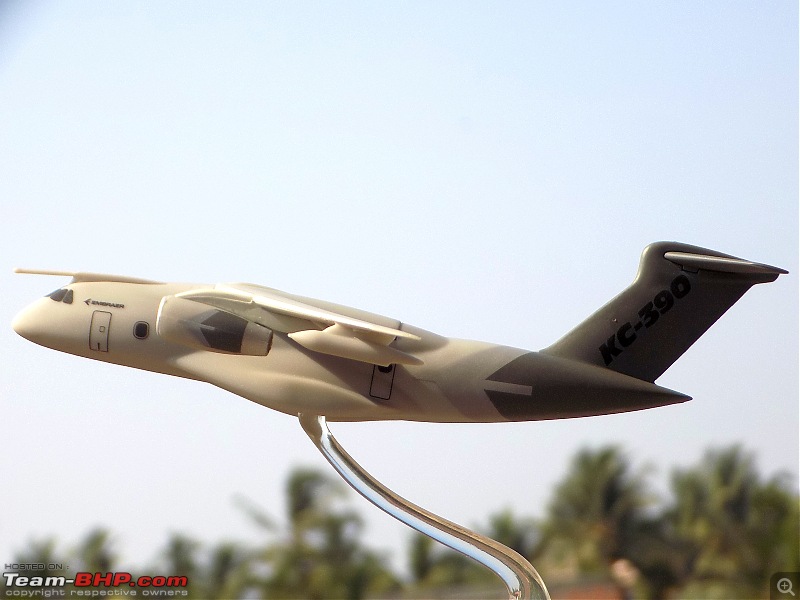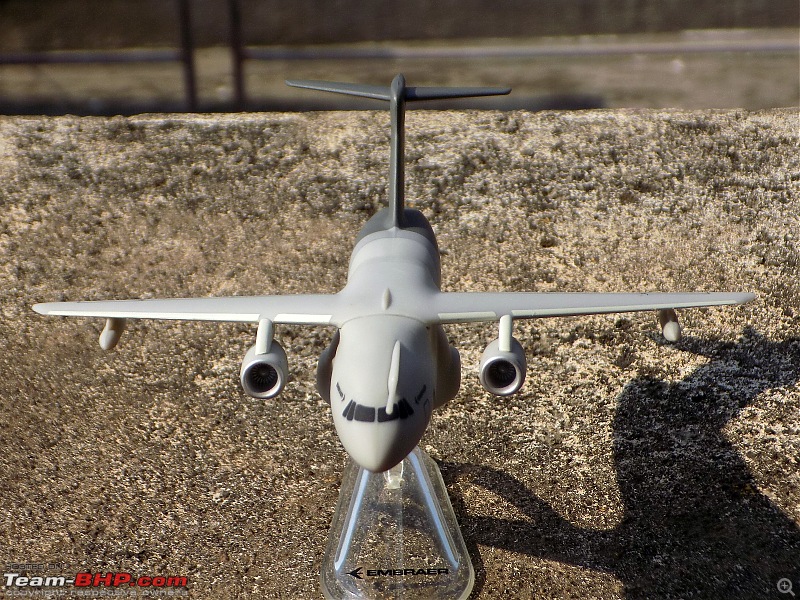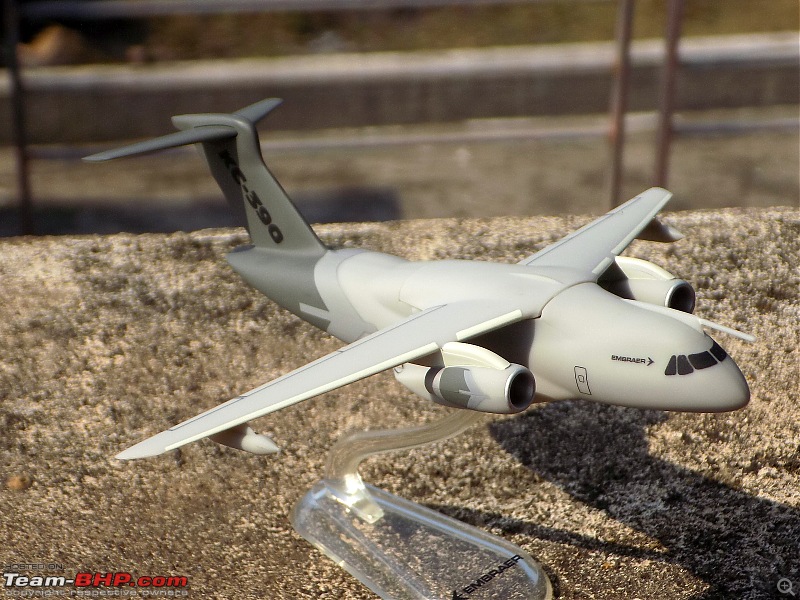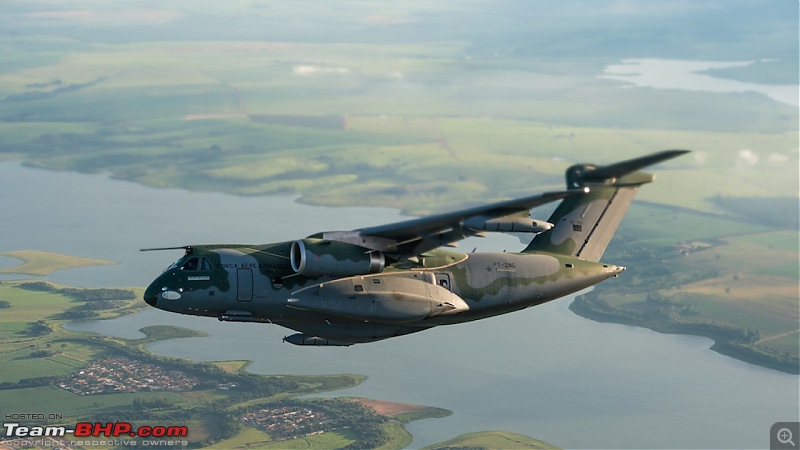           |
| |  (2)
Thanks (2)
Thanks
|
| The following 2 BHPians Thank skanchan95 for this useful post: | badboyscad, V.Narayan |
| | #1974 |
| Senior - BHPian | Re: Scale Models - Aircraft, Battle Tanks & Ships 1:48 Bell UH-1C Iroquois/Huey, 240th Assault Helicopter Company "Greyhounds & Mad Dogs", Camp Bearcat, Binh Hoa, Vietnam, United States Army,1968 The UH-1 was the US Army's first operational turboshaft-powered helicopter, the Bell UH-1 "Huey", would prove one of the most successful rotorcraft in history, with over 16,000 built. The Huey was and remains a common sight in many of the world's military forces, and still is in first-line service in the US Marines. The UH-1 has long been a symbol of US involvement in Southeast Asia in general and Vietnam in particular, and as a result of that conflict, has become one of the world's most recognized helicopters. In Vietnam primary missions included general support, air assault, cargo transport, aeromedical evacuation, search and rescue, electronic warfare, and later, ground attack. UH-1s tasked with ground attack or armed escort were outfitted with rocket launchers, grenade launchers, and machine guns. As early as 1962, UH-1s were modified locally by the companies themselves, who fabricated their own mounting systems.[24] These gunship UH-1s were commonly referred to as "Frogs" or "Hogs" if they carried rockets, and "Cobras" or simply "Guns" if they had guns.UH-1s tasked and configured for troop transport were often called "Slicks" due to an absence of weapons pods. Slicks did have door gunners, but were generally employed in the troop transport and medevac roles. The UH-1C, with a more powerful engine, modified intake system fitted with prominent air filters; and a new "Model 540" rotor system, with a blade chord increased further to 68 centimeters, was introduced in September 1965, but only about 766 were built, since by that time Bell was getting ready to introduce the optimized AH-1 "Cobra" gunship, which was based on UH-1C technology. The "Cobra", as it was actually known in service, provided greater speed and maneuverability and, with its narrow cross-section, was a much more difficult target than the Huey gunships. The Huey gunship would still have its partisans, since its door gunners could lay down fire towards the rear of the helicopter and also provided extra sets of eyes. Huey gunships would actually remain in service in Vietnam up to the end of the war, if mainly due to the fact that there weren't enough Cobras to replace them. The Vietnam War saw the first large-scale use of helicopters in a combat role.Air cavalry, airmobile helicopter formations were widely used by the U.S. Army during the Vietnam War (1954–75) to locate and assault enemy ground forces and transport U.S. troops into battle. The Helicopters(UH-1s) were also used for ammunition supply medevac missions in the battle zone. The slow UH-1s were very vulnerable to enemy ground fire and many and many were show down. The UH-1 pilots saved thousands of lives while performing their job. One in eighteen UH-1 pilots did not make it back home alive. 240th AHC In 1968, the 240th were located at Camp Bearcat, Binh Hoa Province, Vietnam. Bearcat was located near Saigon on Highway One. Known as the “Greyhounds, Mad Dogs, and Kennel Keepers,” the 240th operated UH1C gunships, armed with mini-guns and rockets in the gun platoon, call sign “Mad Dog” and a transport or slick platoon flying UH1H slicks, call sign “Greyhound.” The maintenance platoon was known as the “Kennel Keepers.” The UH-1 featured prominently in great Vietnam War movies like Platoon, Apocalypse Now, We were Soldiers.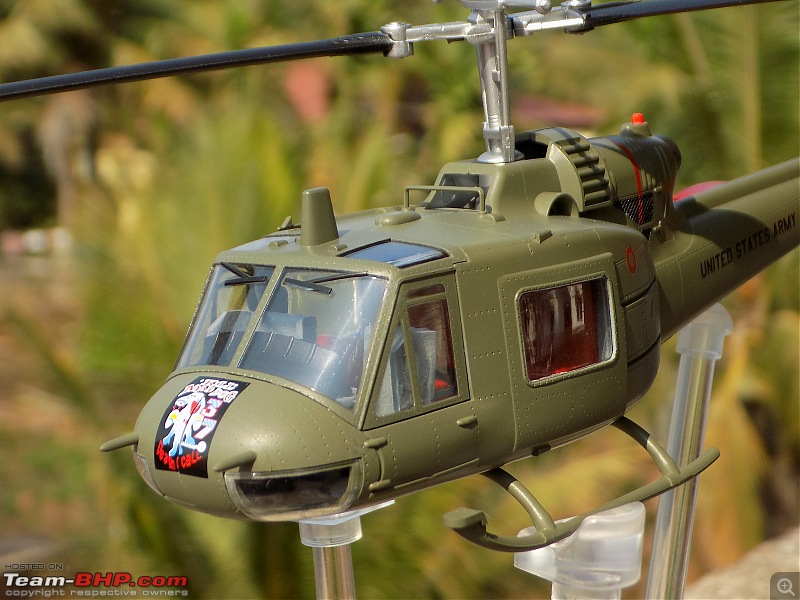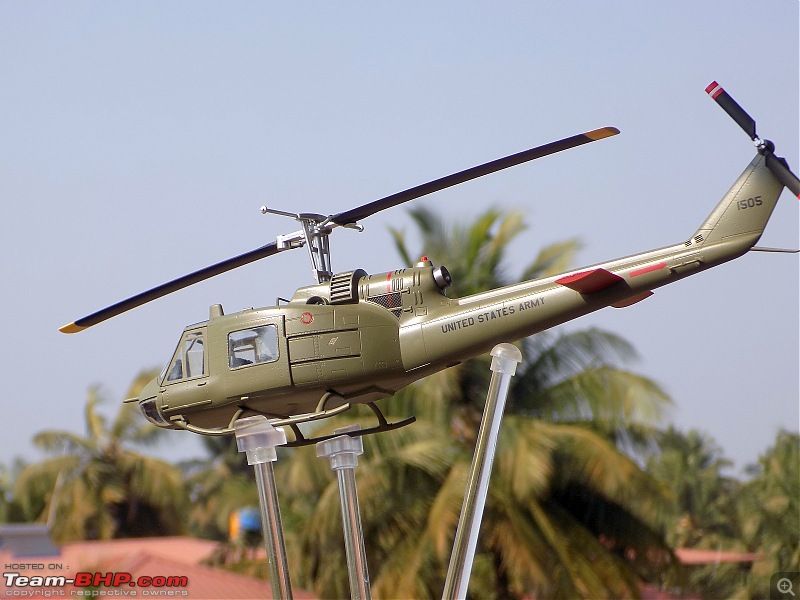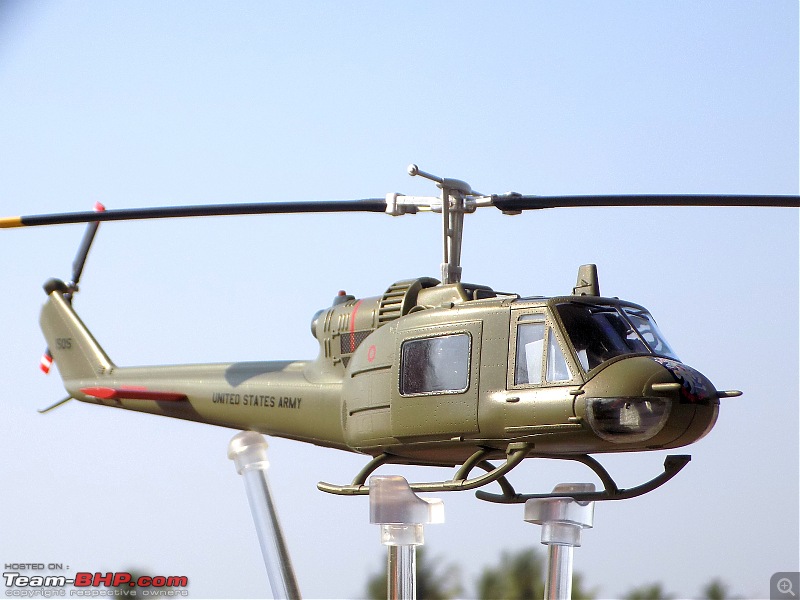         A great book in which the author describes in great detail about his experiences as a UH-1 pilot in Vietnam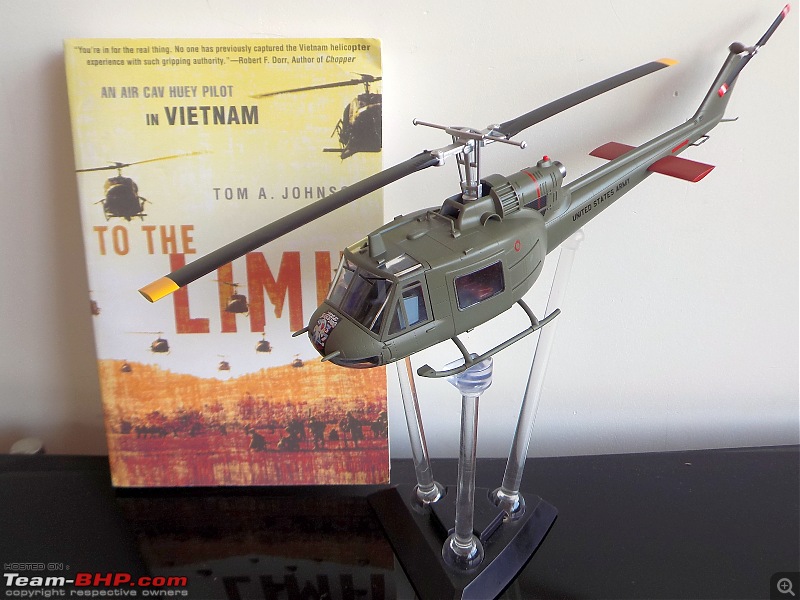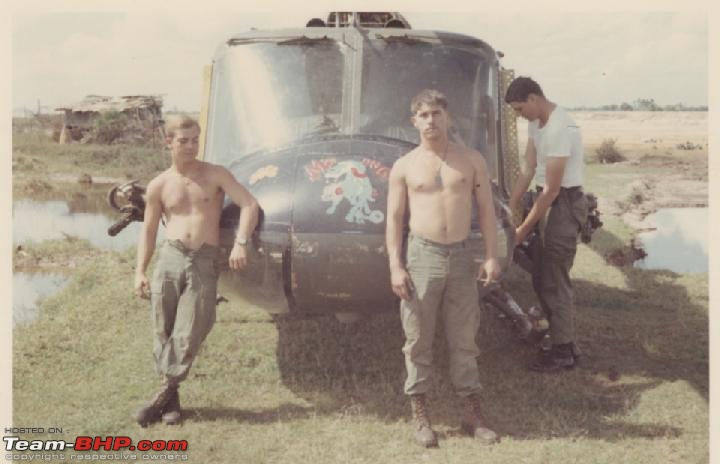     Last edited by skanchan95 : 14th February 2023 at 17:03. |
| |  (3)
Thanks (3)
Thanks
|
| The following 3 BHPians Thank skanchan95 for this useful post: | badboyscad, Foxbat, V.Narayan |
| | #1975 |
| Senior - BHPian | Re: Scale Models - Aircraft, Battle Tanks & Ships 1:100 Dassault Mirage 2000D 133-XK/671 3/3 Escadron de Chasse "Ardennes", Armée de l'air et de l'espace (French Air and Space Force -AAE) The Mirage 2000D is a twin seat conventional attack version of the Mirage 2000N Nuclear Strike fighter. It was designed for long-range precision strikes with conventional weapons. The aircraft is nearly the same as the Mirage 2000N, but introduces support for conventional attack missiles such as the Apache and Scalp missiles, as well as the AASM weapons. Externally the Mirage 2000D could be distinguished from the Mirage 2000N based on the livery and the pitot tube. The Mirage 2000D has a wraparound Grey/Green livery and did not have a pitot tube on the nose, while the Mirage 2000N had Grey/Green livery but with white undersides and a black nose cone with pitot tube. Just like the Mirage 2000B trainer( based on which the Mirage 2000N was developed), the Mirage 2000D does not have an internal cannon. The Mirage 2000D/N was designed for low-level flight and was fitted with an Antilope 5 radar, which is used for terrain following, navigation and ground mapping, and which can follow terrain at 1,112 km/h (691 mph). Apart from terrain following feature of the Antilope 5 radar(the radar sees up to 7 nm in front of the plane, allowing a 600kt speed at 200ft), the radar modes also include Ground mapping & target ranging, Air to sea and Air to air mode( Range 16 miles) The Terrain Following Radar (TFR) allows the autopilot to fly the aircraft very close to the ground. It uses forward-looking radar and the radar altimeter to paint a picture of what the terrain ahead looks like, and sends this information to the autopilot to allow it to fly the aircraft in a straight line at a constant altitude over the ground. It is called "terrain following" because it maintains the same radar altitude regardless of the actual shape of the terrain - therefore the aircraft autopilot will climb over hills and descend into valleys while using TFR.  TFR equipped strike aircraft like the Mirage 2000Ds can fly at low level(also called Nap of the Earth) to avoid enemy detection and attack in a high-threat environment. During NOE flight, geographical features are used as cover, exploiting valleys and folds in the terrain by flying extremely low over them. This keeps the aircraft below enemy air defence radar coverage and avoiding being silhouetted against the sky. The Mirage 2000D complemented Armee de l'Air(French Air Force) SEPECAT Jaguar A daylight strike fighters by providing a night/bad weather attack capability. Formal development began of the Mirage 2000D from the Mirage 2000N began in 1988. The designation was changed to "Mirage 2000D" in 1990, with the "D" standing for "Diversifie/Multi-role". Initial flight of the Mirage 2000D prototype, a modified Mirage 2000N prototype, was on 19 February 1991. That led to first flight of a production aircraft on 31 March 1993, and introduction to service in April 1995. 86 were built in all to last delivery in 2001. The Mirage 2000D could carry Magic II missiles(MICA IR from 2020 onwards on upgraded airframes),dumb bombs, rocket pods,AS-30L ASMs, Laser guided bombs( with weapons guided by a LDP like ATLIS II), SCALP Cruise missiles etc. The WSO in the back seat handled laser targeting/weapons employment while the pilot in the front flies the aircraft. Mirage 2000D in action From 1994 to 1996, French Mirage 2000Ds participated in Operation Deny Flight and Deliberate Force operations in Bosnia & Herzegovina. French Mirage 2000Ds served in the intervention in Afghanistan from 2001, operating in close conjunction with international forces and performing precision attacks with LGBs. On 20 October 2011, a Mirage 2000D dropped the last NATO munitions of the NATO-led 2011 Military intervention in Libya, when a mixed formation of a French Air Force Mirage 2000D and a Mirage F1CR was vectored to strike an armed convoy which was trying to break through the rebels lines at Sirte. The Mirage 2000D dropped its two laser guided GBU-12 bombs hitting and stopping Gaddafi's convoy, resulting in his capture and death. Mirage 2000Ds also took part in operations against ISIL in Iraq & Syria. 3/3 Escadron de Chasse "Ardennes" 3/3 "Ardennes fighter squadron" is a combat unit of the French air force. Currently based at Nancy – Ochey Air Base, and using two-seat Mirage 2000D all-weather attack aircraft.  Specifications (Mirage 2000D/N) General characteristics Crew: 2 Length: 14.55 m (47 ft 9 in) Wingspan: 9.13 m (29 ft 11 in) Height: 5.15 m (16 ft 11 in) Wing area: 41 m2 (440 sq ft) Empty weight: 7,600 kg (16,755 lb) Gross weight: 10,680 kg (23,545 lb) Max takeoff weight: 17,000 kg (37,479 lb) Powerplant: 1 × SNECMA M53-P2 afterburning turbofan engine, 64 kN (14,000 lbf) thrust dry, 95.1 kN (21,400 lbf) with afterburner Performance Maximum speed: 2,338 km/h (1,453 mph, 1,262 kn) Combat range: 1,480 km (920 mi, 800 nmi) Ferry range: 3,340 km (2,080 mi, 1,800 nmi) Service ceiling: 18,000 m (59,000 ft) Rate of climb: 285 m/s (56,100 ft/min) Wing loading: 410 kg/m2 (84 lb/sq ft) Thrust/weight: 0.91 Armament Hardpoints: 4× under-wing, 4× under fuselage, 1× centerline , with provisions to carry combinations of: A2A missiles: R550 Magic II /MICA EM A2G missiles: Apache, SCALP EG, AS-30L Bombs: Dumb bombs, LGBs, GPS guided bombs Rocket Pods : SNEB 68-mm Gun Pods: up to 2× 30 mm CC630 gun pods with 600 rounds per pod, one on each inboard wing hardpoint Targeting Pods: ATLIS II/Damocles Drop Tanks : 1x centerline mounted 345-gallon drop tank and/or 2x either 375, 440 or 530 gallon tanks for ferry flight/extended range/loitering time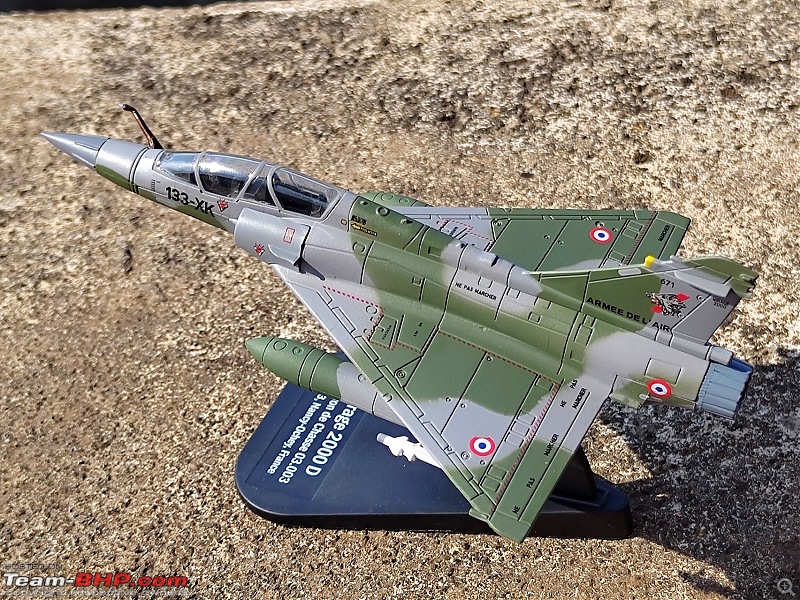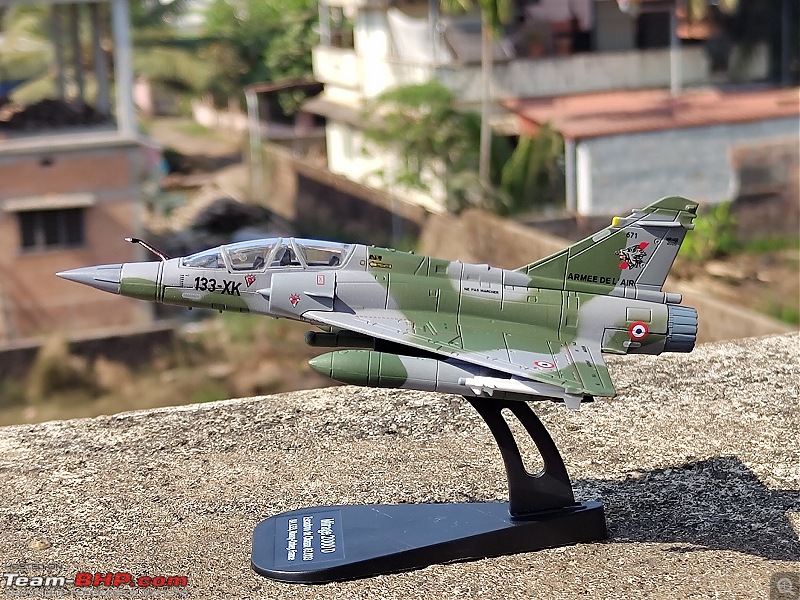   Bomb markings on the nose signifying the number of bombs dropped by the aircraft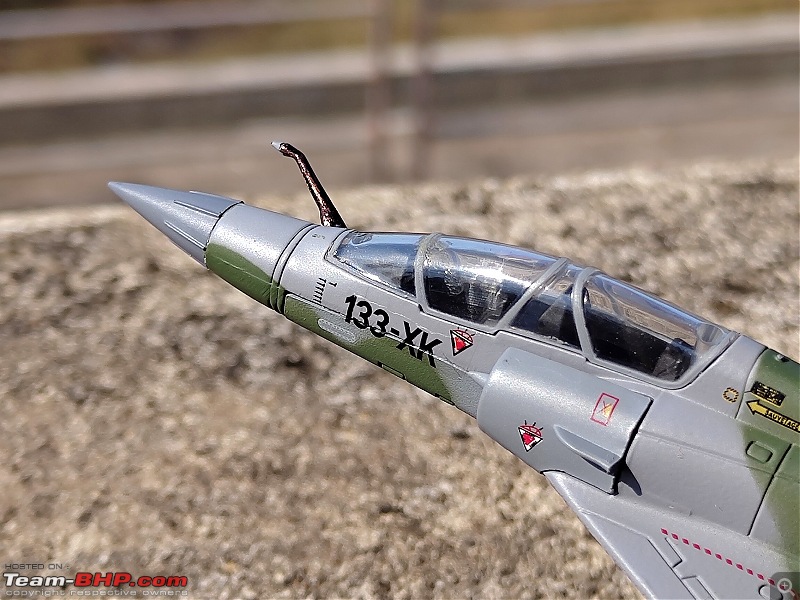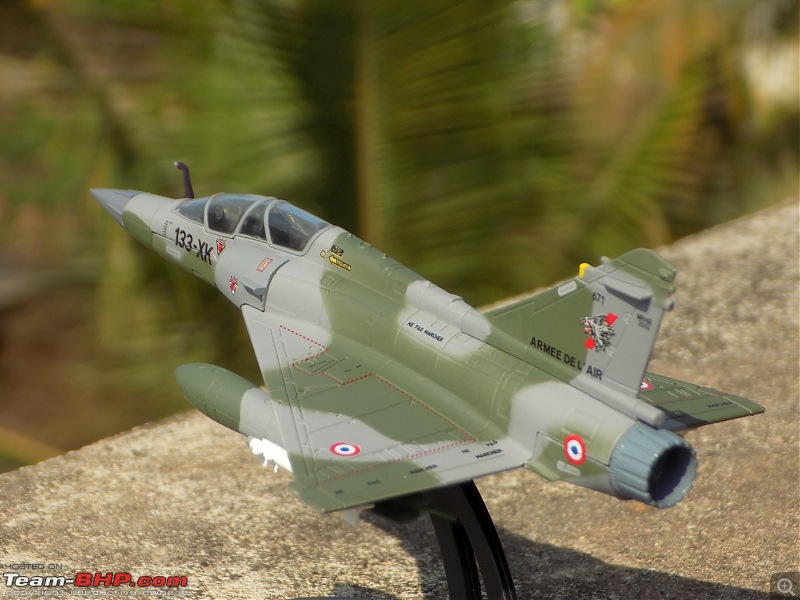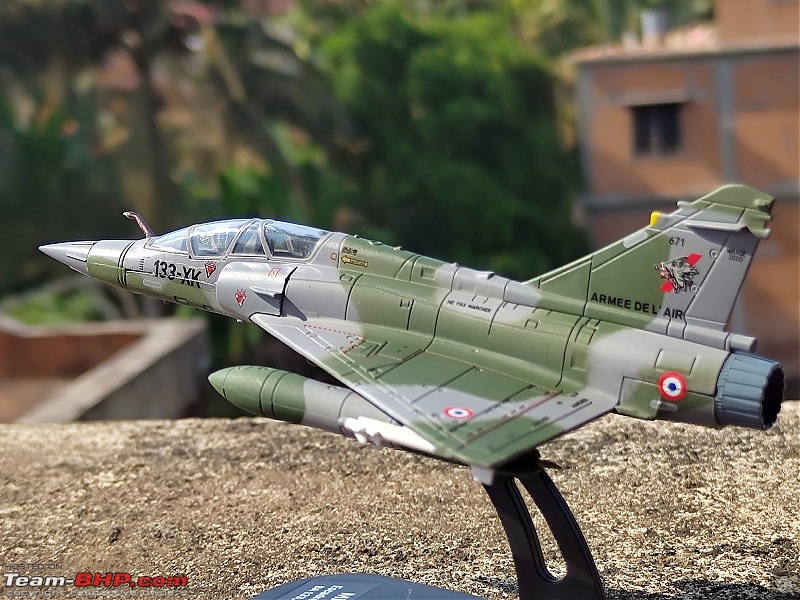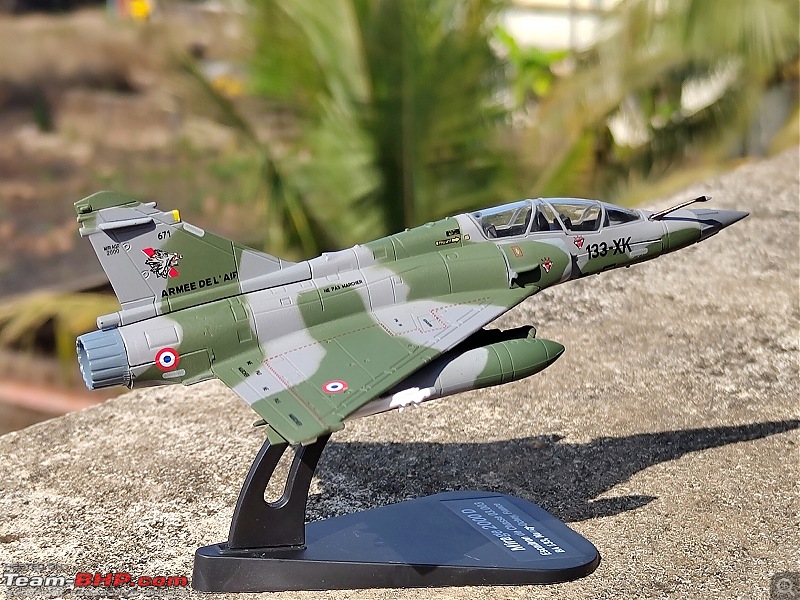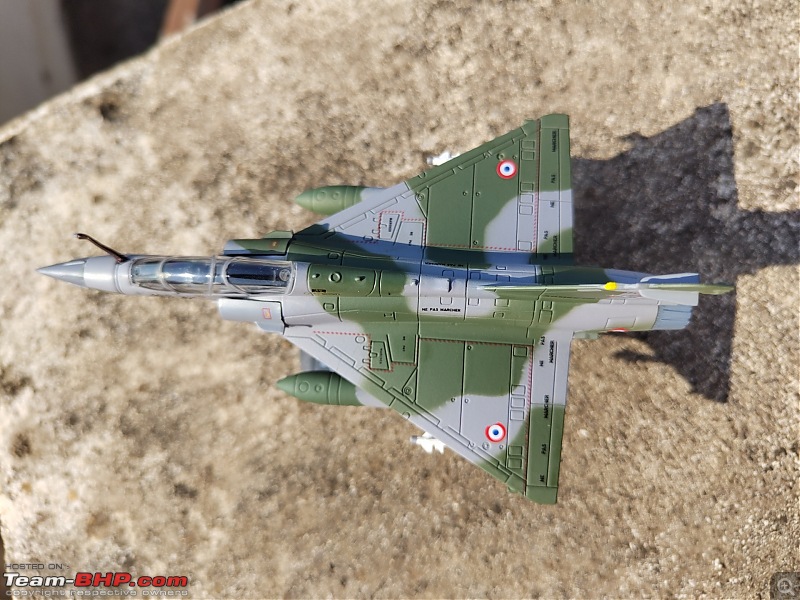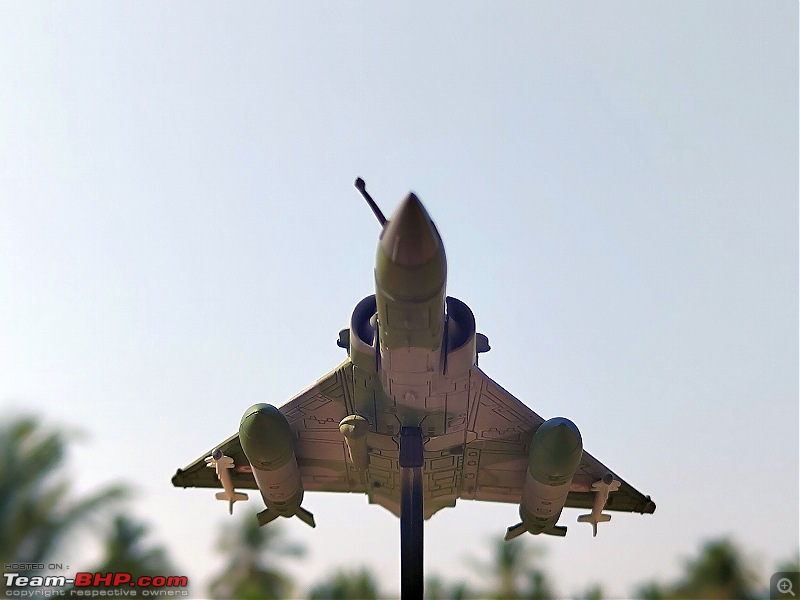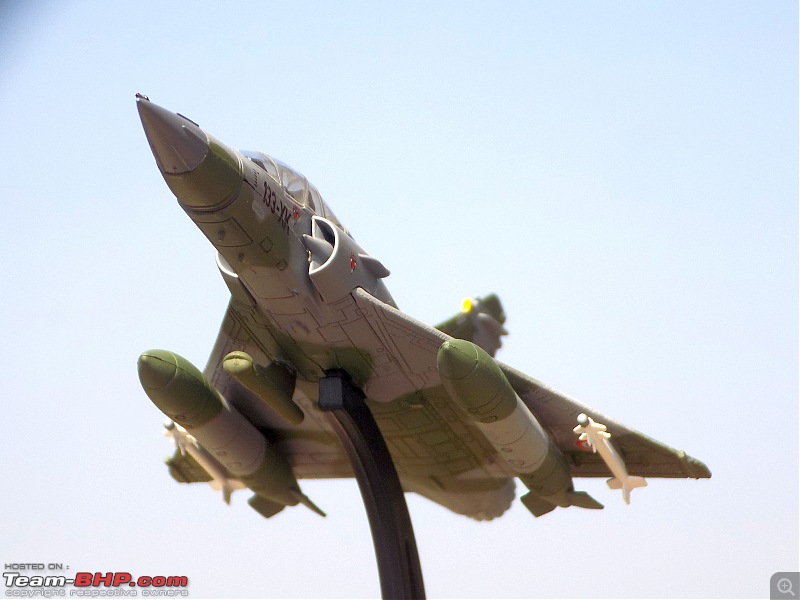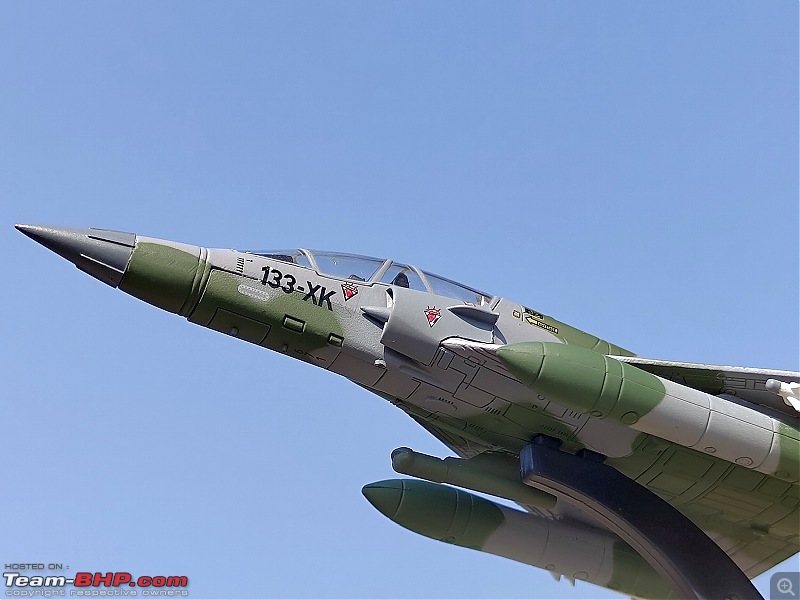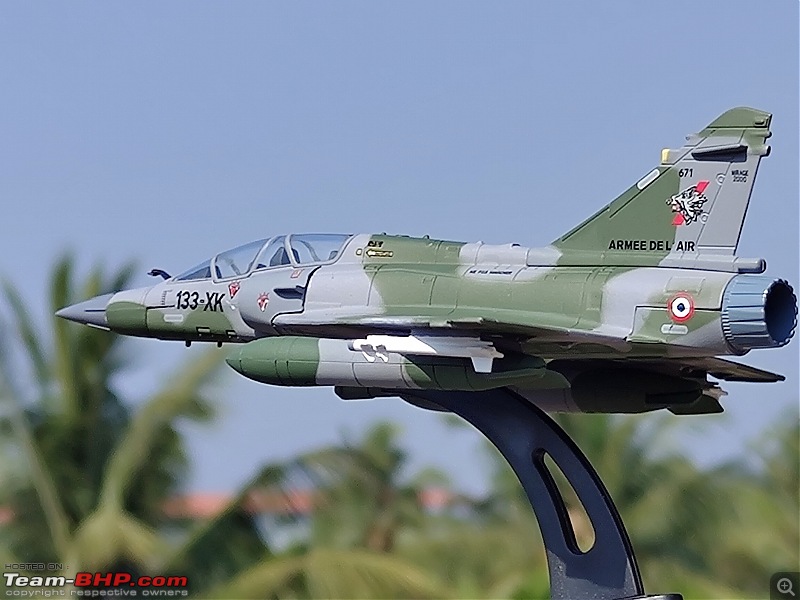           |
| |  (4)
Thanks (4)
Thanks
|
| The following 4 BHPians Thank skanchan95 for this useful post: | badboyscad, Foxbat, Jeroen, V.Narayan |
| | #1976 | |||
| Distinguished - BHPian  Join Date: Aug 2014 Location: Delhi-NCR
Posts: 4,330
Thanked: 72,462 Times
| Re: Scale Models - Aircraft, Battle Tanks & Ships
What a find Sandesh!!!  Just the aircraft we should be license building in India to replace our ageing fleet of An-32s. Just the aircraft we should be license building in India to replace our ageing fleet of An-32s.Quote:
In terms of sheer longevity the UH-1 is up there with the Alouette III in being mid-1950s designs still in ample service almost 7 decades later. The emperor of them all is the Mil Mi-8/Mi-17 the most produced chopper ever and still in production. Like the Alouette III these old helicopters had to be hand flown every minute of the way unlike modern designs like our Dhruv/Rudra. Quote:
Great addition to your collection Sandesh and as always I'm full of praise for your photography. For its era and even for today the 2000D was loaded with the latest avionics to deliver its mission flying a terrain masked mode. Quote:
 looking forward to further updates. looking forward to further updates. | |||
| |  (2)
Thanks (2)
Thanks
|
| The following 2 BHPians Thank V.Narayan for this useful post: | Jeroen, skanchan95 |
| |
| | #1977 | ||
| Senior - BHPian | Re: Scale Models - Aircraft, Battle Tanks & Ships Quote:
 As per a little birdie, Embraer conducted a demo flight of the C-390 with top IAF honchos onboard at Aero India '23. Quote:
 | ||
| |  (1)
Thanks (1)
Thanks
|
| The following BHPian Thanks skanchan95 for this useful post: | V.Narayan |
| | #1978 | |
| Distinguished - BHPian  Join Date: Aug 2014 Location: Delhi-NCR
Posts: 4,330
Thanked: 72,462 Times
| Re: Scale Models - Aircraft, Battle Tanks & Ships Quote:
| |
| |  (1)
Thanks (1)
Thanks
|
| The following BHPian Thanks V.Narayan for this useful post: | skanchan95 |
| | #1979 | |
| Senior - BHPian | Re: Scale Models - Aircraft, Battle Tanks & Ships Quote:
Yes, C-295 + C-390 + C-17 would be ideal. | |
| |  (1)
Thanks (1)
Thanks
|
| The following BHPian Thanks skanchan95 for this useful post: | V.Narayan |
| | #1980 |
| Distinguished - BHPian  Join Date: Aug 2014 Location: Delhi-NCR
Posts: 4,330
Thanked: 72,462 Times
| Re: Scale Models - Aircraft, Battle Tanks & Ships
You are not incorrect in assuming that the C-295 replaces the An-32 as their payload & range is similar. What has happened as a natural progression is that what is considered utility or tactical or medium has moved to the right. In 1961 a 5 tonne payload machine like the HS748 was a utility transport today the same is a 7-tonne C-295 machine. Similarly the 16-tonne An-12 was a medium lifter in 1960s but that has moved to the 23-tonne payload C390 and so on. Since the retirement of the An-12's in the early 1990s we have been sorely missing that useful 16 to 20 tonne lifter. |
| |  (2)
Thanks (2)
Thanks
|
| The following 2 BHPians Thank V.Narayan for this useful post: | FrozeninTime, skanchan95 |
 |